Authors
Gupta, Preeti MD MPH 1; Yamanaka, Travis MD 1 ,2; Kovitz, Kevin MD 1, 3
1 University of Illinois Chicago, Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, Sleep and Allergy, Chicago IL
2 Jesse Brown Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Chicago IL
3 Chicago Chest Center, Elk Grove, IL
Case
A 79-year-old male with a past medical history of Alzheimer’s dementia, chronic respiratory failure with tracheostomy and ventilator dependence, end stage renal disease, and atrial fibrillation is admitted to the intensive care unit from an outside hospital with septic shock. Urine cultures were positive for Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium and the tracheal aspirate was positive for Stenotrophomonas, Pseudomonas, and Proteus species. Chest x-ray demonstrated a right pleural effusion, which was present since outside hospital admission two and a half weeks prior. Decision was made to drainto rule out a source of persistent septic shock. Ultrasound guided thoracentesis was performed with ultrasound visualization during therapeutic aspiration. A total of 1400 cc of serous fluid was removed. After the procedure, the patient was briefly hypotensive, which resolved without intervention. Oxygenation remained stable. Pleural studies revealed a paucicellular lymphocytic transudate.
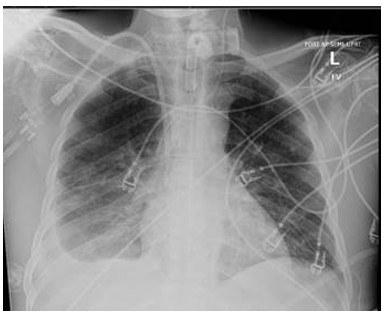
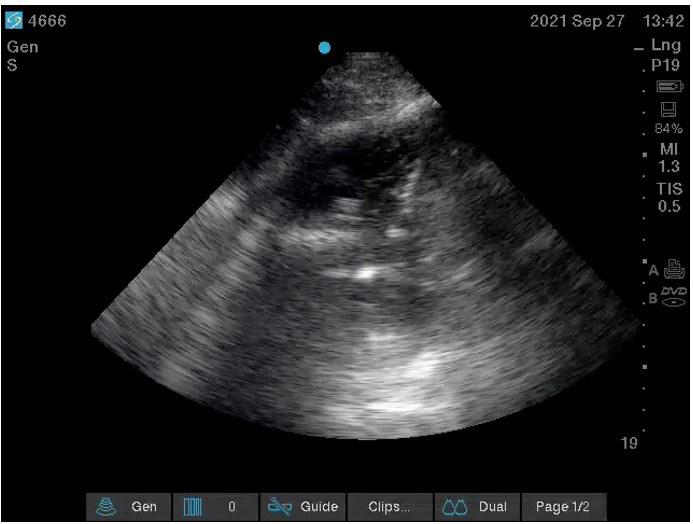
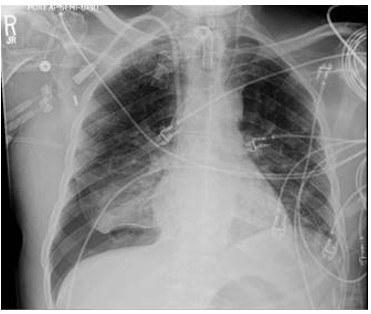
Question
What is the finding?
A. Tension pneumothorax
B. Pneumothorax ex vacuo
C. Re-expansion pulmonary edema
D. Hemothorax
What is the immediate next step?
A. Emergent needle decompression
B. Observation
C. Diuresis
D. Insert a large bore chest tube (28 to 32 French)